HDFS is the main hub of the Hadoop ecosystem, responsible for storing large data sets both structured & unstructured across various nodes & thereby maintaining the metadata in the form of log files. Thus, to work with such a system, we need to be well versed or at least should be aware of the common commands and processes to ease our task. In that matter, we have consolidated some of the most commonly used HDFS commands that one should know to work with HDFS.
To begin with, we need to check the below list.
2. Run Hadoop -- we can use the 'start-all.cmd' command or start directly from the Hadoop directory.
3. Verify Hadoop services -- We can check if our Hadoop is up and running using the below command
jps
Great..!!! Now we are ready to execute and learn the commands.
**Note:- These commands are case-specific. Do take special care of capital and small letter while writing the commands.
1. version -- this command is used to know the version of our Hadoop, with additional local file system location and compilation information.
hadoop version
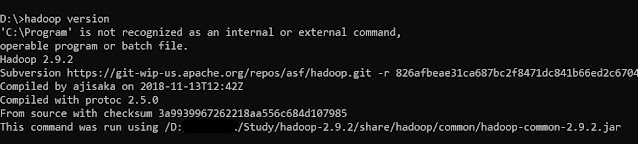 |
| Hadoop version |
2. mkdir -- this command is used to create a new directory, if it does not exists. If the directory exists, it will give a "File already exists" error.
hadoop fs -mkdir <Directory Path/Name>
| Hadoop mkdir |
3. ls -- this command is used to check the files or directory in the HDFS. It shows the name, permissions, owner, size, and modification date for each file or directory in the specified directory.
hadoop fs -ls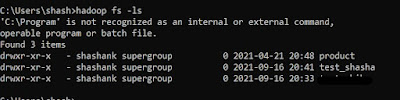 |
| Hadoop ls |
4. put -- this command is used to copy the data from the local file system to HDFS.
hadoop fs -put <Local File Path> <HDFS file path>
| Hadoop put |
We can verify the same from HDFS WebUI.
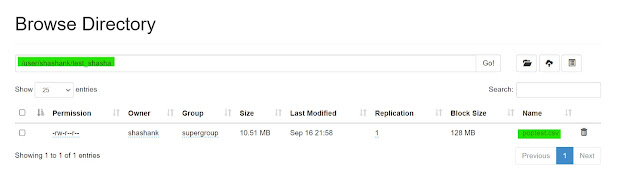 |
| Hadoop put WebUI |
5. get -- this command is used to copy the data from HDFS to the local file system. This command is the reverse of the 'put' command.
hadoop fs -get <HDFS file path> <Local File Path>
| Hadoop get |
We can verify the same from our local file system.
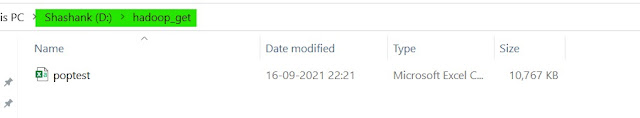 |
| Hadoop get WebUI |
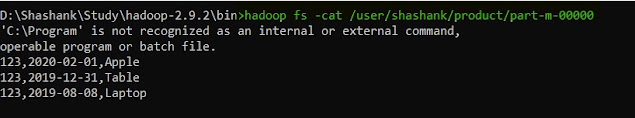
6. cat -- command used to view the data from the file in HDFS
hadoop fs -cat <HDFS file path with file name>
 |
| Hadoop cat |
7. mv -- this command is used to move a file from one location to HDFS to another location in HDFS.
hadoop fs -mv <Source HDFS path> <Destination HDFS path>
 |
| Hadoop mv |
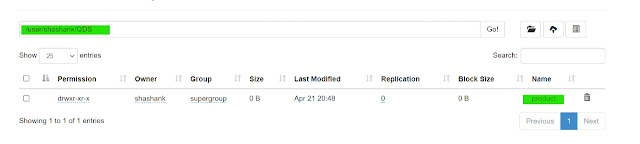
we can verify the same from Web UI.
 |
| Hadoop mv WebUI |
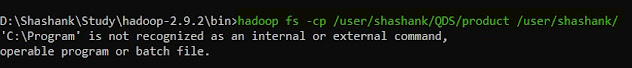
8. cp -- this command is used to copy a file from one location to HDFS to another location within HDFS only.
hadoop fs -cp <Source HDFS path> <Destination HDFS path>
 |
| Hadoop cp |
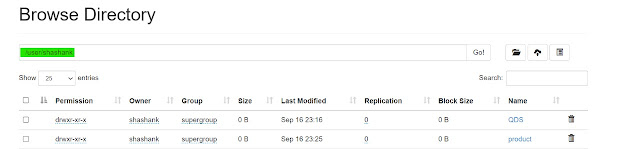
we can verify the same from Web UI.
 |
| Hadoop cp WebUI |
9. copyFromLocal -- this command is used to copy data from the local file system to HDFS.
hadoop fs -copyFromLocal <Local File Path> <HDFS file path>
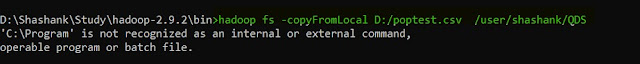 |
| Hadoop copyFromLocal |
We can verify the copied file from WebUI.
10. copyToLocal -- this command is used to copy data from HDFS to the local file system.
hadoop fs -copyToLocal <HDFS file path> <Local File Path>
 |
| Hadoop copyToLocal |
We can check the file in our local file system.
11. moveFromLocal -- this command is used for moving a file or directory from the local file system to HDFS.
hadoop fs -moveFromLocal <Local File Path> <HDFS file path>
 |
| Hadoop moveFromLocal |
12. moveToLocal -- this command is used for moving a file or directory from HDFS to the local file system. This command is yet not implemented, but soon will be.
hadoop fs -moveToLocal <HDFS file path> <Local File Path>
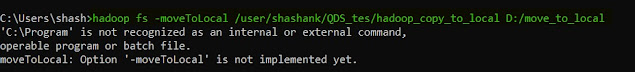 |
| Hadoop moveToLocal |
13. rm -- removes, this command is used to delete/remove a file from HDFS.
hadoop fs -rm <HDFS file path>
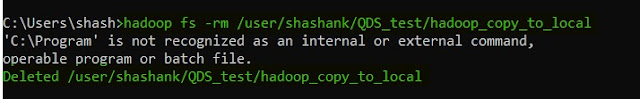 |
| Hadoop rm |
14. tail -- this command is used to read the tail/end part of the file from HDFS. It has an additional parameter "[-f]", that is used to show the appended data to the file.
hadoop fs -tail [-f] <HDFS file path>
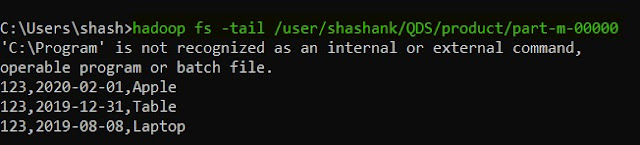 |
| Hadoop tail |
15. expunge -- this command is used to make the trash empty.
hadoop fs -expunge
 |
| Hadoop expunge |
16. chown -- we should use this command when we want to change the user of a file or directory in HDFS.
hadoop fs -chown <HDFS file path>
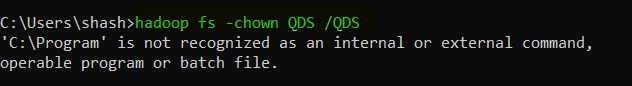 |
| Hadoop chown |
We can verify if the user changed or not using the hadoop -ls command or from WebUI.
 |
| Hadoop chown WebUI |
17. chgrp -- we should use this command when we want to change the group of a file or directory in HDFS.
hadoop fs -chgrp <HDFS file path>
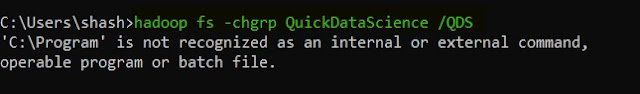 |
| Hadoop chgrp |
We can verify if the user changed or not using the hadoop -ls command or from WebUI.
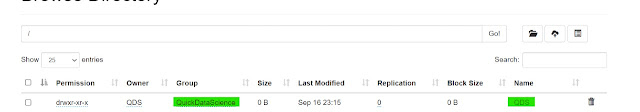 |
| Hadoop chgrp WebUI |
18. setrep -- this command is used to change the replication factor of a file in HDFS.
hadoop fs -setrep <Replication Factor> <HDFS file path>
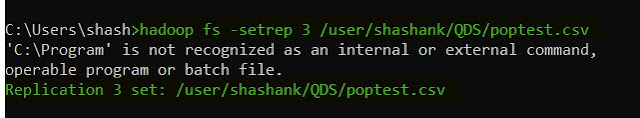 |
| Hadoop setrep |
We can check it from the WebUI.
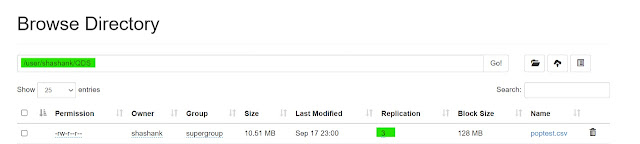 |
| Hadoop setrep WebUI |
19. du -- this command is used to check the amount of disk usage of the file or directory.
hadoop fs -du <HDFS file path>
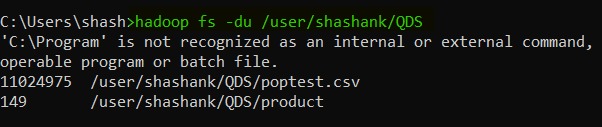 |
| Hadoop du |
20. df -- this command is used to shows the capacity, free space and size of the HDFS file system. It has an additional parameter "[-h]" to convert the data to a human-readable format.
hadoop fs -df [-h] <HDFS file path>
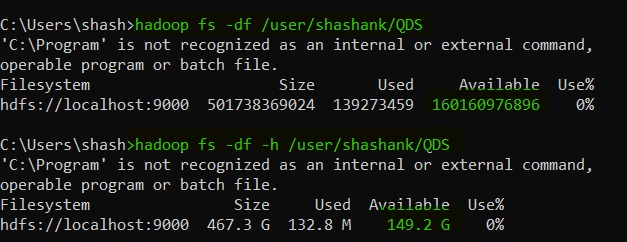 |
| Hadoop df |
21. fsck -- this command is used to check the health of the files present in the HDFS file system.
hadoop fsck <HDFS file path>
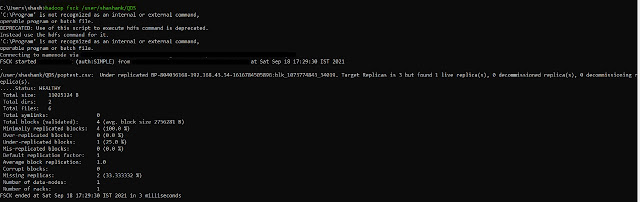 |
| Hadoop fsck |
It also has some attributes/options to modify the command use.
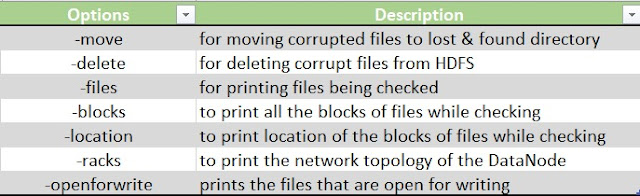 |
| fsck options |
22. touchz -- this command creates a new file in the specified directory of size 0.
hadoop fs -touchz <HDFS file path>
 |
| Hadoop touchz |
The new file can be seen in the WebUI.
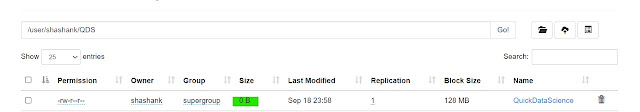 |
| Hadoop touchz WebUI |
23. test -- this command answer various questions about <HDFS path>, with the result via exit status.
hadoop fs -test <HDFS file path>
 |
| Hadoop test options |
24. text -- this is a simple command, used to print the data of an HDFS file on the console.
hadoop fs -text <HDFS file path>
| Hadoop text |
25. stat -- this command provides the stat of the file or directory in HDFS.
hadoop fs -stat <HDFS file path>
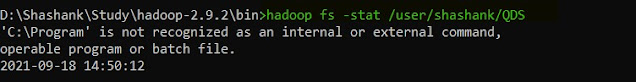 |
| Hadoop stat |
It can provide data in the following formats. By default, it uses '%y'.
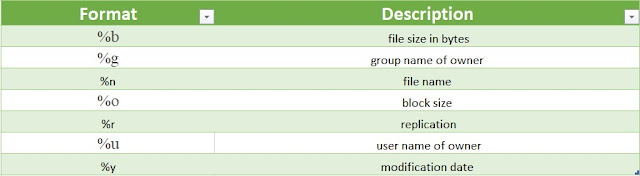 |
| Hadoop stat formats |
26. usage -- Displays the usage for given command or all commands if none is specified.
hadoop fs -usage <command>
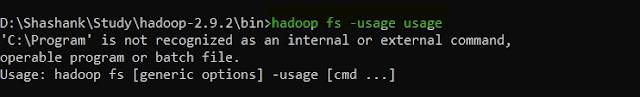 |
| Hadoop usage |
27. help -- Displays help for given command or all commands if none is specified.
hadoop fs -help <command>
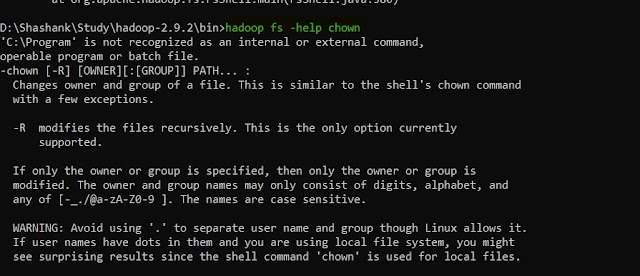 |
| Hadoop help |
28. chmod -- is used to change the permission of the file in the HDFS file system.
hadoop fs -chmod [-r] <HDFS file path>
 |
| Hadoop chmod |
Old Permission
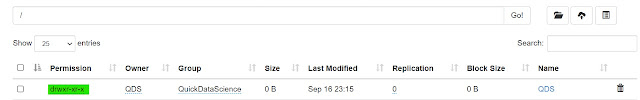 |
| Hadoop chmod Old Permission |
New Permission
| Hadoop chmod New Permission |
29. appendToFile -- this command is used to merge two files from the local file system to one file in the HDFS file.
hadoop fs -appendToFile <Local file path1> <Local file path2> <HDFS file path>
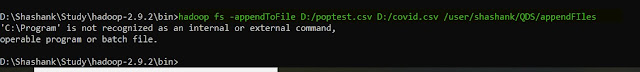 |
| Hadoop appendtofile |
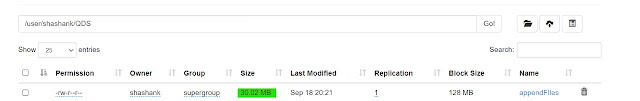 |
| Hadoop appendtofile WebUI |
30. checksum -- this command is used to check the checksum of the file in the HDFS file system.
hadoop fs -checksum <HDFS file Path>
 |
| Hadoop checksum |
31. count -- it counts the number of files, directories and size at a particular path.
hadoop fs -count [options] <HDFS directory path>
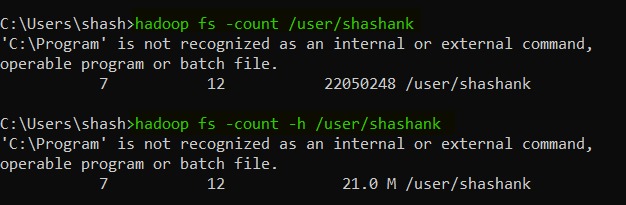 |
| Hadoop count |
This function also has few functions to modify the query as per need.
 |
| Hadoop count options |
32. find -- this command is used to find the files in the HDFS file system. We need to provide the expression that we are looking for and can also provide a path if we want to look for the file at a particular directory.
hadoop fs -find <HDFS directory path> <Expression>
 |
| Hadoop find |
33. getmerge -- this command is used to merge the contents of a directory from HDFS to a file in the local file system.
hadoop fs -getmerge <HDFS directory> <Local file path>
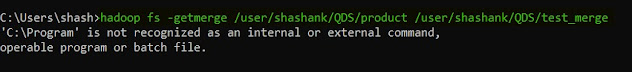 |
| Hadoop getmerge |
The merged file can be seen in the local file system.
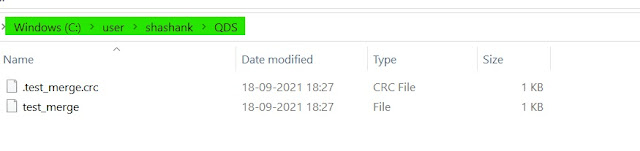 |
| Hadoop getmerge file |
Overview of the HDFS commands.
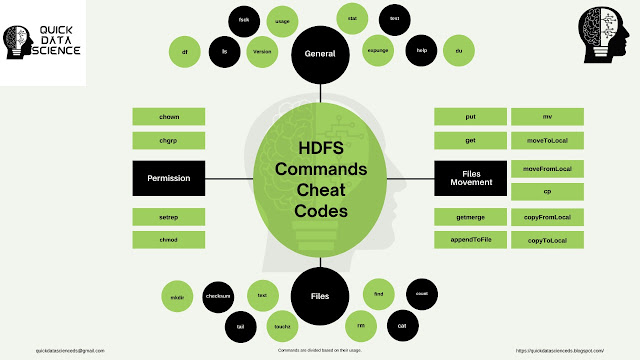 |
| HDFS Commands |
Summary
We learned the most common and frequently used HDFS commands. We have seen how to use them and learned the practical aspects as well.
So don't just read, practice along with us and let us know the issues and challenges if you face any.
Until Then... This is Quick Data Science Team signing off. See you with another article.


Comments
Post a Comment